Optical fibers which are used in optical fiber cable, Integra Cable brand
A – single-mode optical fiber compliant with ITU-T G.652.D standard
A – single-mode optical fiber compliant with ITU-T G.657.A standard
H – single-mode non zero-dispersion shifted optical fiber (NZDSF) compliant with ITU-T G.655 standard
B – multi-mode optical fiber with the core diameters 62.5 µm
M – multi-mode optical fiber with the core diameters 50 µm compliant with ITU-T G.651.1 standard
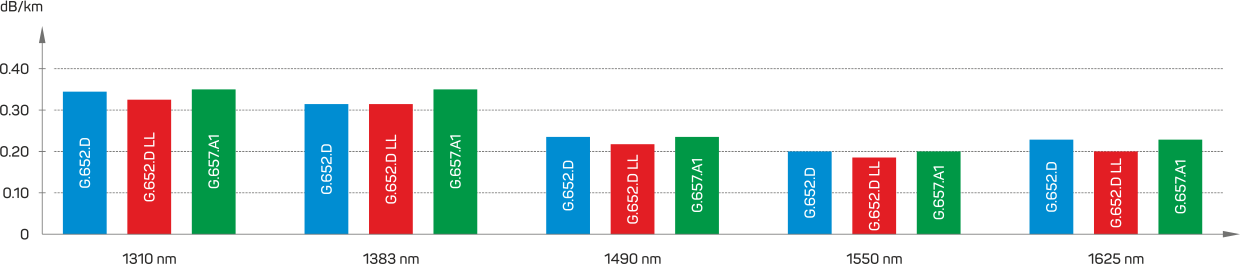
Attenuation at wavelength
G.652. Standard single-mode fiber
These fibers are widely deployed in the public networks and they represent a large majority of fibers that have been installed.
A single-mode optical fiber with zero-dispersion is a key foundation to the modern optical networks that are the basis of all modern telecommunications, it is classified by ITU-T G.652 standard. This fiber is widely used and optimized for the transmission with the wavelength around 1310 nm. The upper limit of the wavelength L-band is 1625 nm. To test the fiber to macro-bending, the mandrel with the radius 30 mm is used.
According to the standard the fibers have four categories A, B, C, D.
The fiber G.652. А meets the requirements applicable for informational flows transmission of the level STM 16, – 10 Gbit/s (Ethernet) for the distance up to 40 km, in accordance with G.691 and G.957 recommendations, and also level STM 256, according to G.691.
The fiber G.652.B meets the requirements applicable for informational flows transmission of the level STM 64 in accordance with G.691 and G.952 recommendations, and also level STM 256, according to G.691 and G.959.1.
G.652.C and G.652.D fibers enable the data transmission in the wider wavelength range from 1360 to 1530 nm, they are also characterized by low water peak (LWP) (water peak of the single-mode fibers is located in the wavelength range from 1300 nm to 1550 nm). Other characteristics of the categories C and D are equal to those of G.652.A and G.652.B.
G.652.A/B is equivalent to OS1 (ISO/IEC 11801 classification), G.652.C/D is equivalent to OS2.
When the higher data transmission speed is required and the distance exceeds 40 km, the use of the fiber G.652 leads to the disagreement between the performance efficiency and single-mode fiber standards and as a result, it requires complex endpoint equipment.
Standard optical fiber scheme in optical module
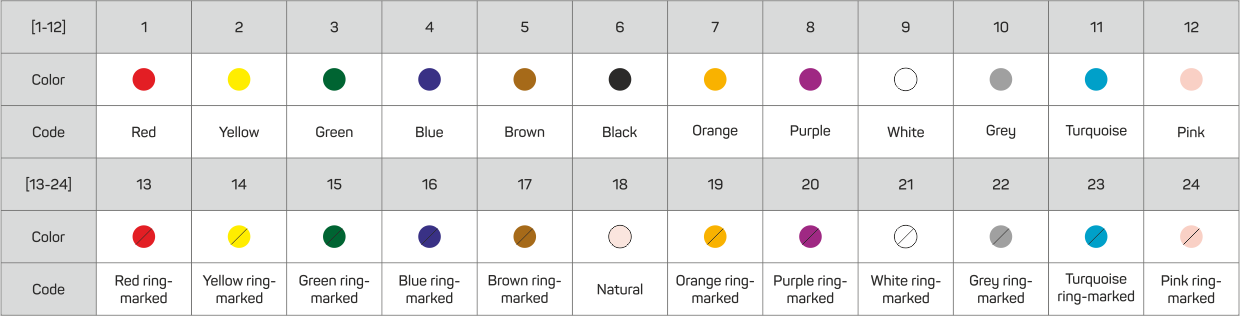
When using more than 12 optical fibers in the tube, the fibers from 13 to 24 have additional color ring marks. It is done to distinguish all 24 fibers. According to the customer requirements different color coding of fibers and tubes can be used. Instead of the blind tubes PE fillers can be used in the cable constructions when necessary.
G.655. Single-mode non zero-dispersion shifted fiber (NZDSF)
Single-mode non zero-dispersion shifted fiber is optimized for the transmission of different wavelengths (Wavelength Division Multiplexing WDM and Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing DWDM). The Corning fiber has a double acrylate coating which provides high efficiency and reliability. The outer coating diameter is 245 Mcm.
NZDSF is especially designed for trunk optical fiber lines and global communication networks, which use DWDM-technology. This fiber maintains a limited chromatic dispersion coefficient throughout the entire optical region used in wavelength division multiplexing (WDM). NZDSF fibers were intended for use in a prescribed region between 1530 nm and 1565 nm.
The recommendations divide the fibers into three categories – A, B, C; these categories have different polarization mode dispersion coefficients, chromatic dispersion and wavelength range.
Characteristics of the G.655.A optical fibers enable to use them in the single-channel and multi-channel systems with optical amplifiers (recommendations G.691, G.692, G.693) and in optical transport networks (recommendation G.959.1). The operating wavelengths and fiber dispersion of this category limit the input power thus restricting their use in the multi-channel systems.
The optical fibers G.655.B are similar to G.655.A. But depending on the operating wavelengths and dispersion characteristics, the input power can be higher than for G.655.A. The operating distance of 400 km for STM-64 level systems can be provided according to the requirements applied to Polarization Mode Dispersion.
The G.655.C fibers are similar to G.655.B, but more stringent requirements regarding Polarization Mode Dispersion enable to use STM-256 level systems with G.655.C optical fibers (G.959.1 recommendation) either to increase the transmission distance of the STM-64 systems.
Color coding according to TIA/EIA-598 standard
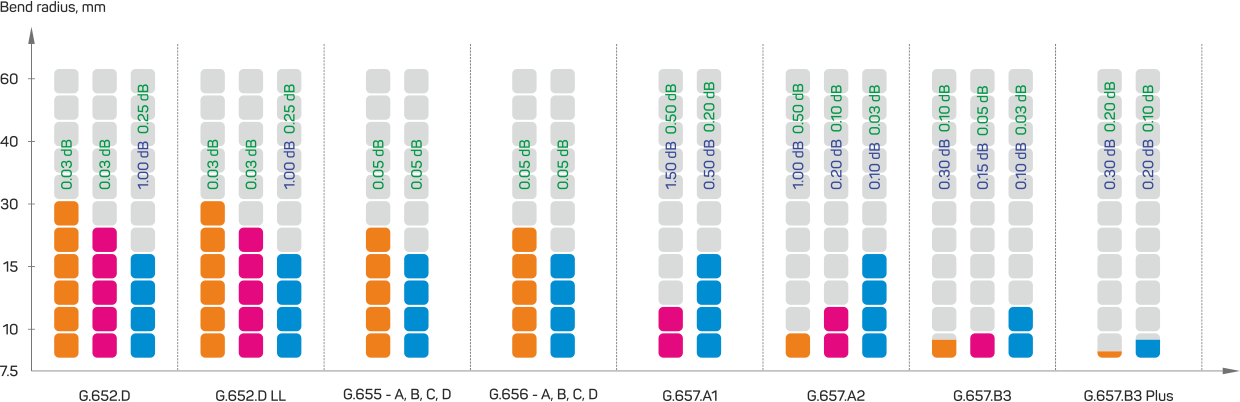
G.657. Bend-insensitive single-mode optical fiber
The bend-insensitive single-mode optical fiber G.657 is widely implemented in the indoor cables installed in the networks of multi-story building, business complexes etc. The fiber G.657.A in it’s optical characteristics is absolutely similar to the standard fiber G.652.D, at the same time the fiber G.657.A has a twice less permitted bending installation radii – 15 mm. The fiber G.657.B is used for short distance connections and has extra low bending losses.
Single-mode optical fibers with low bending losses are designed for the FTTH networks of the multi-story buildings, the advantages of these fibers are revealed in the restricted space. The operating rules for G.657 fiber is almost identical to those of the copper-core cable.
The fiber G.657 is divided into categories A and B, the difference among them is in the core diameter and the minimum bending radius performance.
The core diameter for G.657.A is from 8.6 to 9.5 µm, the core diameter for G.657.B is from 6.3 to 9.5 µm.
The standards for macro-bending losses were significantly tightened since this parameter is crucial for G.657:
– ten turns of the fiber G657.A about the mandrel with the radius 15 mm should not exceed the attenuation coefficient value of 0.25 dB at the wavelength 1550 nm. A single turn of the same fiber about the mandrel with the diameter 10 mm should not exceed the attenuation coefficient value of 0.75 dB, providing that the other parameters are not changed;
– ten turns of the fiber G.657.B about the mandrel with the radius 15 mm should not exceed the attenuation coefficient value of 0.03 dB at the wavelength 1550 nm. A single turn of the fiber about the mandrel with the diameter 10 mm should not exceed the attenuation coefficient value of 0.1 dB, about the mandrel with the diameter 7.5 mm should not exceed the attenuation coefficient value of 0.5 dB.
ITU G.657.А standard prioritizes compatibility with standard fibers over functionality (ITU G.652.D standard). ITU-T G.657.В standard focuses on insensitivity to bending, but not on compliance with the requirements of standards G.652.
Dependence of the max attenuation on the bend radius at 1550 and 1625 µm
OM1 and OM2. Standard multi-mode fibers with the core diameters 62.5 µm and 50 µm respectively
Cables, patch cords and pigtails with multi-mode fibers of the types OM1 62.5/125µm and OM2 50/125µm have been used for a long time in the SCS for data transmission at high speed and at relatively long distances, which are required in the trunk lines. The most important operating parameters of the MM-fibers are attenuation and overfilled mode bandwidth. Both parameters are determined for wavelengths of 850 nm and 1300 nm, these lengths are used by the largest part of the active network equipment.
This multi-mode fiber is especially designed for Gigabit and 10 Gigabit Ethernet networks, the only core diameter available is 50 µm.
OM4. «Laser-optimized» multi-mode optical fiber with the core diameter 50 µm
OM4 type multi-mode fiber is now fully corresponds to modern standards for the optical fibers designed for data processing centers and server groups of the next generation. OM4 optical fiber can be used to build more extended lines in the new generation data transmission networks with the highest transmission performance. This fiber is the result of further optimization of OM3 fiber characteristics, making it possible to achieve the data transmission speed of 10 GB/s over 550 meters. OM4 fiber types are characterized by higher minimal overfilled mode bandwidth of 4700 MHz/km at a wavelength of 850 nm (compared to 2000 MHz/km OM3 type fiber).
Standard colors of optical tube in the cable core
Optical tube identification goes from red tube forward green one.